Decoding The Characteristics Of Asteroid Glaucus

Introduction
The asteroid Glaucus is an intriguing celestial object that has captivated astronomers and researchers alike. In this article, we will delve into the unique characteristics of Glaucus and explore its significance in the realm of asteroids.
A Brief Overview of Asteroid Glaucus

Composition and Size
Glaucus is classified as a C-type asteroid, indicating that it is primarily composed of carbonaceous materials. This composition suggests a rich abundance of organic compounds and water ice, making Glaucus a potential resource for future space missions and exploration.
Orbit and Rotation
Glaucus orbits the Sun within the main asteroid belt, situated between Mars and Jupiter. Its orbital period is approximately 4.72 years. In terms of rotation, Glaucus completes a full spin on its axis in about 6 hours, giving it a relatively fast rotational speed.
Physical Features
Glaucus has an irregular shape with an oblong or elongated appearance. Its surface is likely characterized by numerous impact craters, evidence of its long celestial journey and encounters with other objects in space.
The Significance of Asteroid Glaucus
Potential Insights into Solar System Formation
Studying asteroids like Glaucus can provide valuable insights into the early formation of our solar system. The composition and structure of C-type asteroids can reveal information about the processes that occurred billions of years ago during the birth of the planets.
Potential Resources and Future Exploration
As mentioned earlier, Glaucus holds promise as a potential resource for future space exploration missions. Its carbonaceous composition and the presence of water ice make it an attractive target for mining operations and the extraction of valuable materials.
Understanding Impact Risks
Asteroids like Glaucus also serve as important reminders of the potential impact risks they pose to Earth. Studying their orbits and trajectories can help scientists develop strategies for potential asteroid deflection or mitigation measures in the future.
The Future of Asteroid Glaucus Research

Ongoing Investigations
Scientists around the world continue to study Glaucus through ground-based telescopes, space-based observations, and even robotic missions. These investigations aim to gather more detailed information about its composition, structure, and potential resources.
Upcoming Missions
There are plans for future missions to explore Glaucus up close. These missions will provide unprecedented opportunities to study this intriguing asteroid and possibly even bring back samples to Earth for further analysis.
Collaborative Efforts
The study of asteroids like Glaucus requires collaboration between various scientific disciplines. Astronomers, planetary scientists, engineers, and space agencies all work together to unlock the mysteries of these cosmic objects and expand our understanding of the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions

-
What is the composition of asteroid Glaucus?
Glaucus is primarily composed of carbonaceous materials, suggesting the presence of organic compounds and water ice.
-
Where does asteroid Glaucus orbit?
Glaucus orbits the Sun within the main asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter.
-
What is the potential significance of studying asteroids like Glaucus?
Studying asteroids like Glaucus can provide insights into the early formation of the solar system, potential resources for future space exploration, and risks associated with asteroid impacts on Earth.
-
Are there any upcoming missions planned to explore Glaucus?
Yes, there are plans for future missions to study Glaucus up close and potentially bring back samples to Earth.
-
How do scientists study asteroids like Glaucus?
Scientists study asteroids through ground-based telescopes, space-based observations, and robotic missions.
Conclusion
Glaucus, with its unique characteristics and potential resources, offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of asteroids. Through ongoing research and upcoming missions, scientists are poised to uncover even more about this celestial object and its significance in understanding our cosmic origins. As we continue to explore the mysteries of asteroids, we invite you to share your thoughts and engage with Asteroid Realm by subscribing to our website, sharing this article, and joining the discussion in the comments section. Thank you for joining us on this journey through the captivating realm of asteroids.
Additional Resources
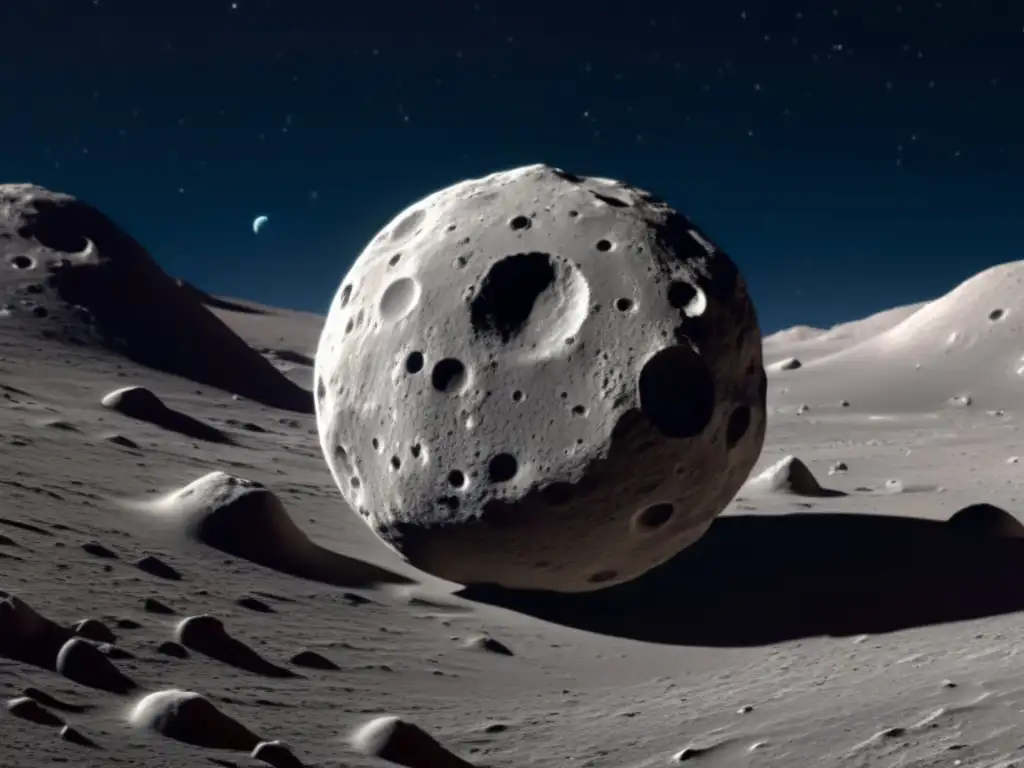

To delve deeper into the topic of asteroids, we recommend the following resources:
 The Surprising Features Of Asteroid Lycaon
The Surprising Features Of Asteroid Lycaon The Role Of Asteroid Telemachus In Astronomy
The Role Of Asteroid Telemachus In Astronomy Asteroid Dolon: A Tale Of Discovery
Asteroid Dolon: A Tale Of DiscoveryIf you want to discover more articles similar to Decoding The Characteristics Of Asteroid Glaucus, you can visit the Asteroid Profiles category.
Leave a Reply

Articulos relacionados: